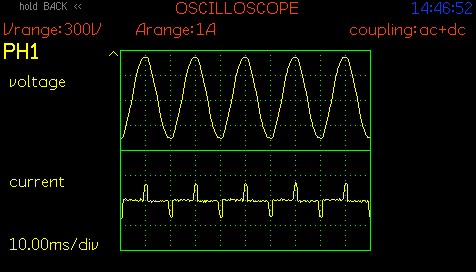
When it comes to the quality assessment of LED drivers, most purchasers will instantly think about terms like driver efficiency, power factor or isloted/non-isolated driver designs. A less observed but certainly not less important factor is the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD), a measure used to assess the distortion introduced into an electrical signal by harmonic components. Harmonic components in electrical systems originate from various sources, including nonlinear loads, power electronic devices, imperfect power generation and distribution equipment.
When an electrical signal deviates from a perfect sine wave, it can introduce harmonic frequencies that are multiples of the fundamental frequency. These harmonics can distort the waveform and affect the quality of the signal. THD is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by comparing the root mean square (RMS) value of all harmonic components to the RMS value of the fundamental frequency.
Harmonic distortions can cause various issues with LED lighting systems, namely the efficiency of LED lighting power supplies, leading to increased power consumption and energy wastage. THD affects the power factor, which measures how effectively electrical power is utilized. A low power factor resulting from high THD can lead to increased electricity costs and reduced overall system efficiency.
Excessive harmonic distortion can also stress components within the LED lighting power supply, potentially leading to premature failure or degradation of performance. LEDs are sensitive to fluctuations in voltage and current, and high THD levels can cause irregularities in the power supply that may impact the lifespan and reliability of LED fixtures.
Harmonic distortion can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can interfere with other electronic devices and communication systems. LED lighting power supplies with high THD levels may emit electromagnetic noise that disrupts nearby equipment, affects wireless communication, or violates regulatory standards for electromagnetic compatibility.
Another point is the compliance with regulatory standards. Standards set by organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), often impose limits on harmonic distortion to ensure the quality of electrical power and minimize interference with the electrical grid. LED lighting power supplies must comply with these standards to ensure safe and reliable operation and avoid potential penalties or restrictions on product distribution.
Finally LED lighting systems often incorporate dimming and control features for adjusting light levels and creating different ambiance settings. High THD levels can affect the performance and accuracy of dimming controls, leading to flickering, uneven brightness, or compatibility issues with dimmer switches and control systems.